Measles cases increased 80 per cent over the last year, other diseases could follow: UN
- Covid interrupted schemes for routine vaccinations around the world, putting the health of millions of people – mainly children – at risk
- Countries facing conflict, such as Somalia, Yemen, and Afghanistan, reported the highest number of cases; officials fear the numbers could soar in Ukraine
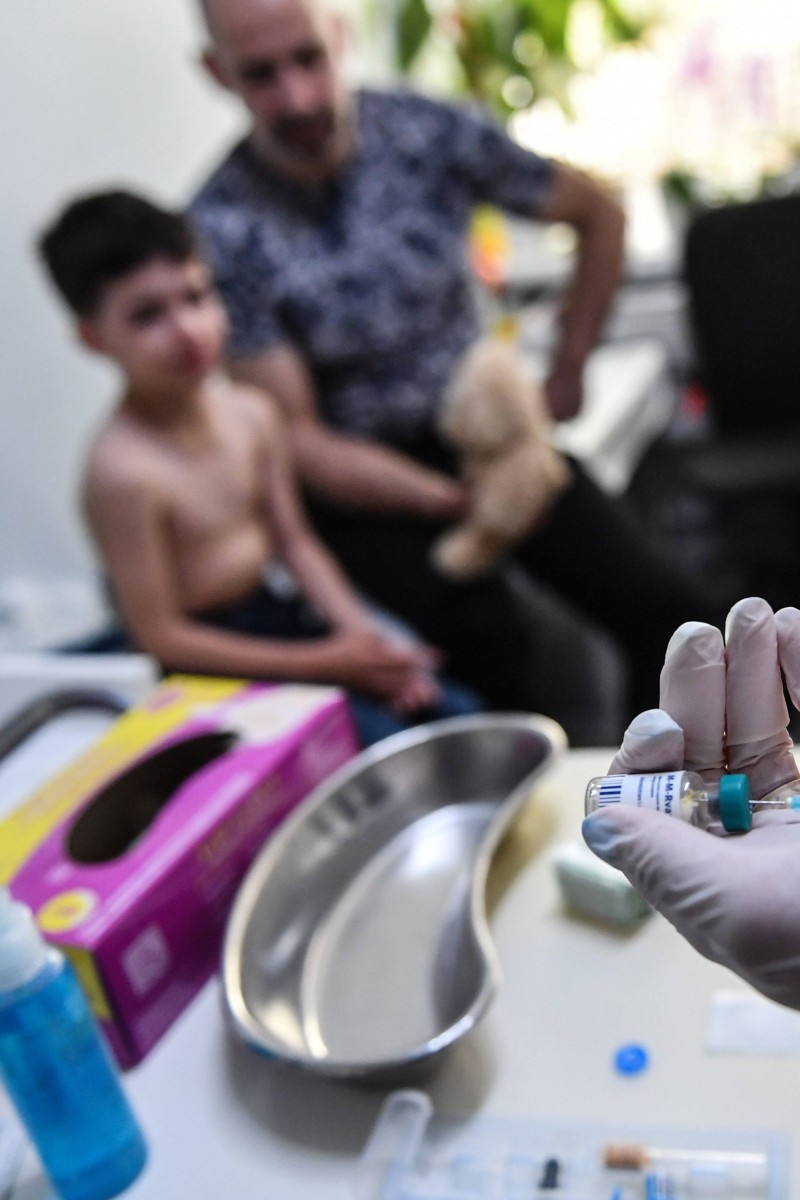
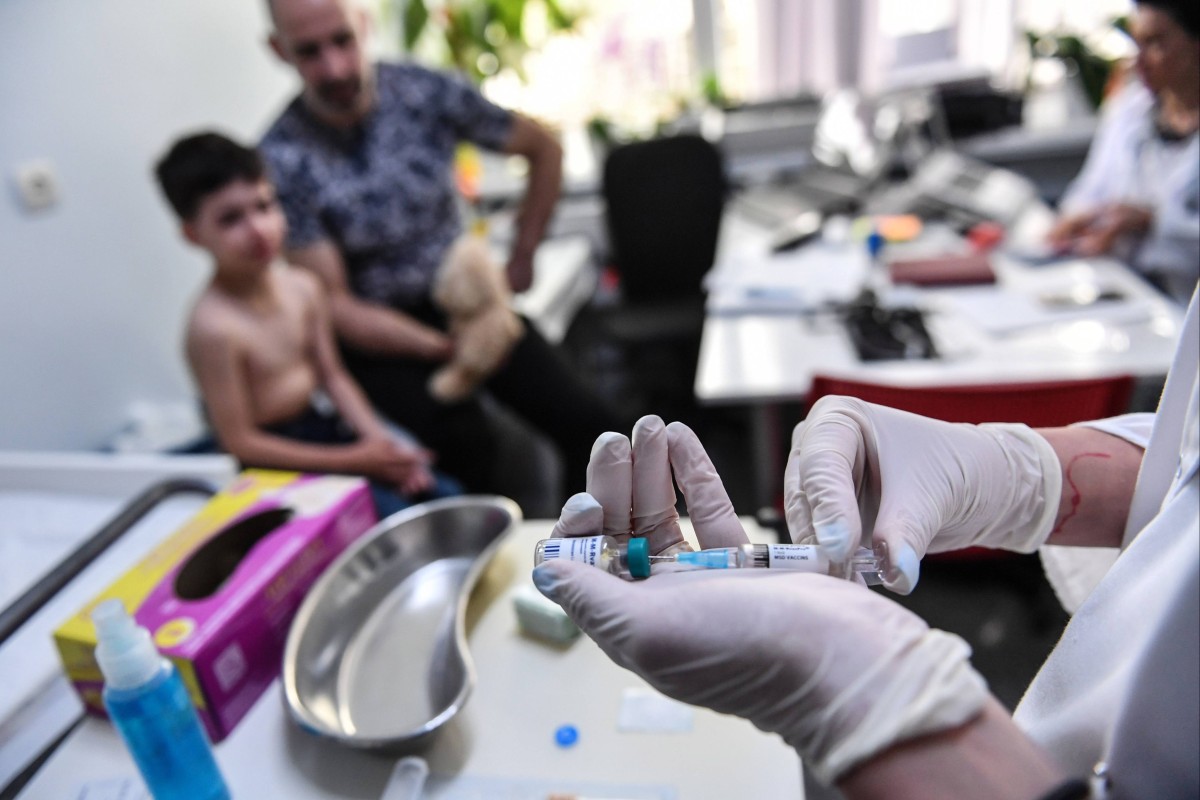 A family physician prepares a measles vaccine during a consultation in the Romanian capital of Bucharest in 2018. The coronavirus pandemic has interrupted vaccination campaigns for other childhood diseases, such as measles, leading to an increase in cases. Photo: Daniel Mihailescu/AFP via Getty Images
A family physician prepares a measles vaccine during a consultation in the Romanian capital of Bucharest in 2018. The coronavirus pandemic has interrupted vaccination campaigns for other childhood diseases, such as measles, leading to an increase in cases. Photo: Daniel Mihailescu/AFP via Getty ImagesCases of the measles cases have surged by nearly 80 per cent worldwide this year, the United Nations (UN) said on Wednesday, warning that the rise of the illness indicates that outbreaks of other diseases are likely on the way.
The coronavirus pandemic has interrupted vaccination campaigns for non-Covid diseases around the world, creating a “perfect storm” that could put millions of children’s lives at risk, the UN’s children’s agency Unicef and the World Health Organization (WHO) said in a statement.
More than 17,300 measles cases were reported globally in January and February, compared to around 9,600 during those months last year, according to new data from the UN agencies.
Most kids in the US have had coronavirus, study finds
There have been 21 large and disruptive measles outbreaks in the last 12 months to April, most of them in Africa and the eastern Mediterranean, the data showed.
Christopher Gregory, senior health adviser in Unicef’s immunisation section, said that because measles is the “most contagious vaccine-preventable disease” it often serves as a warning sign.
“Measles is what we call the tracer, or the canary in the coal mine, that really shows us where those weaknesses in the immunisation system are,” he said.
He said yellow fever was among the diseases that could surge next, after rising cases were reported in West Africa.
“We’re particularly worried about those countries that are most fragile, where the healthcare systems are already really struggling, where they’re still trying to deal with the impacts of Covid on top of these outbreaks,” he said.
Somalia recorded by far the most measles cases over the last 12 months with more than 9,000, the UN data showed, followed by Yemen, Afghanistan, Nigeria and Ethiopia – all countries battling some form of conflict.
Why you should still wear your mask on planes
There are also fears that the war in Ukraine could spark a resurgence in the country after it recorded Europe’s highest rate of measles between 2017-2019.
Gregory said that it had been very difficult to keep track of any disease in Ukraine since the war began, adding that the biggest concern was “what we could be missing”.
More than 23 million children missed out on routine vaccinations in 2020 as the Covid pandemic descended, the largest number in more than a decade.
5 tips for patients battling long Covid
The UN agencies said that 57 vaccination campaigns in 43 countries postponed at the start of the pandemic had still not been completed, affecting 203 million people – most of them children.
Covid also continues to pile pressure on healthcare facilities and drag staffing and attention away from vaccination for long-standing deadly diseases.
“The impact of these disruptions to immunisation services will be felt for decades to come,” WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said in the statement.
“Now is the moment to get essential immunisation back on track and launch catch-up campaigns so that everybody can have access to these life-saving vaccines.”
Gregory said it was time to put childhood immunisation on “at least the same level of priority as finishing Covid vaccination”.
Measles is a disease caused by a virus that attacks mainly children. The most serious complications include blindness, brain swelling, diarrhoea, and severe respiratory infections.
Vaccination uptake of at least 95 per cent is the best way to avoid it spreading, though many countries fall far short of that goal – Somalia is at just 46 per cent, according to the UN data.