
What’s the deal with malaria? How does the parasite spread through mosquito bites?
- Check out our graphic to learn more about how people get infected with this disease, and read the article to understand how scientists are stopping it




Difficulty: Challenger (Level 2)
Nearly half a million children in sub-Saharan Africa die every year from malaria. The disease is spread through a parasite carried by mosquitoes.
Malaria is caused by a parasite called Plasmodium. Only female Anopheles mosquitoes can spread it to humans through bites. They do it when they feed, about every seven days.
A mosquito becomes infected after it drinks blood from someone who has malaria. When it bites another person, its saliva injects them with the parasites.
The parasite gets into the blood and enters the liver. It then infects red blood cells. This is usually when people get symptoms (see graphic).
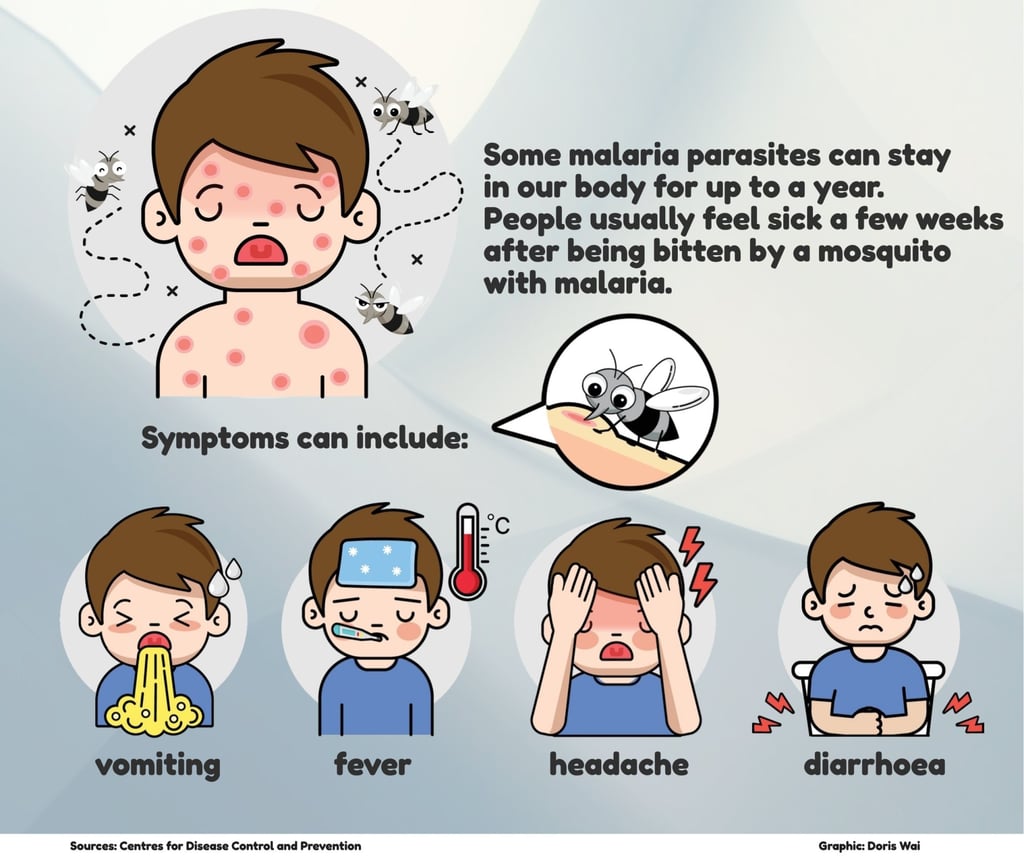
Malaria can also spread from a mother to her unborn baby, through blood transfusions, and by sharing needles used for injecting drugs.
Medicine can help kill the parasite. In 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended a vaccine to prevent malaria in children. It is still new technology, but it could be very helpful.
The head of WHO, Tedros Ghebreyesus, said the vaccine could be combined with tools such as mosquito nets treated with insecticides to prevent malaria. This could save the lives of tens of thousands of children each year.
Questions
-
Can male mosquitoes spread malaria to human beings?
-
Why is the malaria vaccine important?

