Hong Kong’s public universities record the highest number of dropouts since 2004
- More than 2,100 students at the city’s eight publicly funded universities quit in the 2019-20 academic year, up 15 per cent from 2018-19
- Most universities cited personal and family issues as the main reasons behind the withdrawals, but student leaders said politics also played a part
New figures released by the University Grants Committee, the main funding body for the city’s public institutions of higher learning, also showed that some schools were hit harder than others, with one experiencing a 40 per cent increase in dropouts in 2019-20 compared to the previous academic year.
Surge in Hong Kong and mainland students applying for British universities
The dismal figures came hot on the heels of previous surveys showing dozens of primary and secondary schools similarly reporting more students dropping out over the past year, including at traditionally elite institutions, with many of the youths leaving Hong Kong altogether.
“The number of [university] students withdrawing has obviously seen an increase … We also hope to know the exact reasons, but it is not easy,” said Professor Lau Chi-pang, Lingnan University’s associate vice-president of academic affairs and external relations.
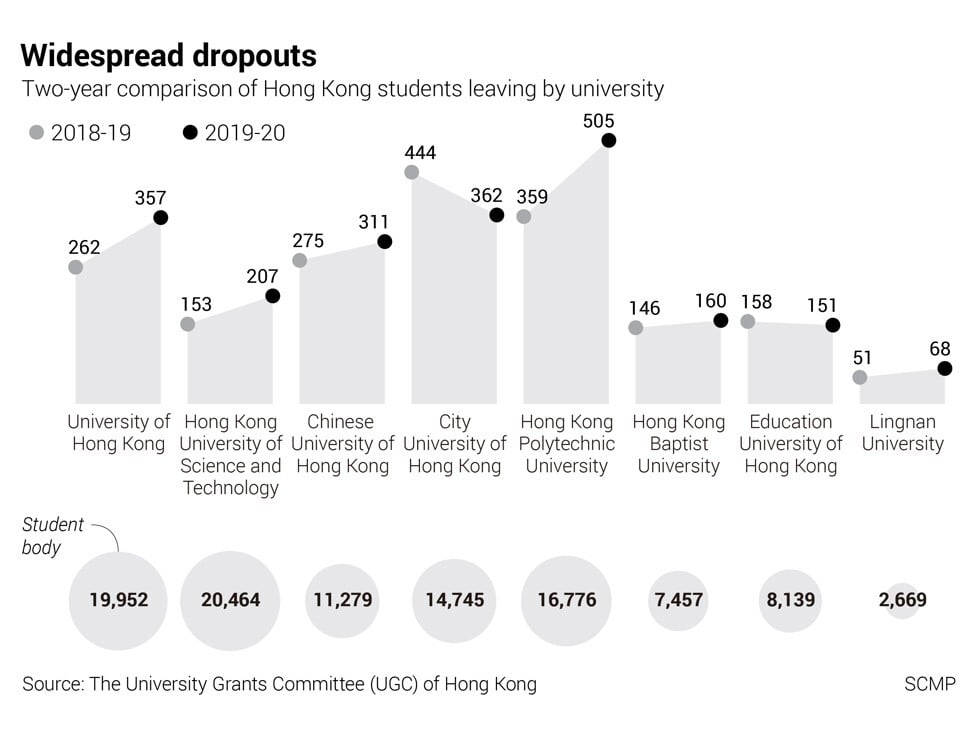
In the 2019-20 academic year, a total of about 2,120 undergraduate and postgraduate students withdrew from the city’s eight publicly-funded universities, up 15 per cent from 1,848 in 2018-19, according to statistics from the grants committee.
City University and Education University were the only public funded institutions that did not see an uptick in dropouts. PolyU, meanwhile, had the most, with 505 students dropping out, about 40 per cent more than the 359 who quit the previous year.
The University of Hong Kong and the University of Science and Technology saw 357 and 207 students withdraw, respectively, up 36 and 35 per cent from 2018-19. Chinese University had 311 students withdraw – a 13 per cent rise.
The grant committee figures included both local and non-local students.
PolyU and Chinese University saw some of the most significant damage during the 2019 social unrest after protesters occupied their campuses and engaged in fiery clashes with police.

Edy Jeh Tsz-lam, a student representative of HKU’s governing council and the former president of its student union, said she believed some of the dropouts could be non-local students returning to their home countries because of the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic, but others were local students who chose to leave Hong Kong and study elsewhere.
She said she had heard of students transferring to universities in Taiwan and Britain, while others had quit university to reapply to study other subjects because of changing personal goals.
“For instance, a friend of mine who was studying law told me [during the 2019 protests] that she was considering quitting university and reapplying for dentistry, as she believed studying law and [entering the legal sector] in Hong Kong was no longer meaningful,” Jeh said, pointing to critics’ remarks about declining confidence in the local judicial system.
PolyU student union president Alan Wu Wai-kuen said he had peers who had chosen to pursue their studies elsewhere after dropping out, including some who had moved to Australia and Canada.
Hong Kong student union quits after university cut links over national security
In replies to the Post, Baptist, Polytechnic, Education and Lingnan universities only cited personal reasons as the main cause of student withdrawals. A Chinese University spokeswoman, however, added that students transferring to other local institutions or overseas universities was also a major factor.
The dropout figures for 2019-20 were highest since the 2003-04 academic year – the earliest for which grants committee data was immediately available. About 1,704 students withdrew from local universities that year, with the number of dropouts ultimately hitting a low of 1,057 in 2010/11. It eventually rose again, however, and has hovered at around 1,800 a year since 2015.
Lau, of Lingnan University – which saw a 33 per cent rise in dropouts in 2019/20 – said studies should be carried out to determine the precise reasons behind students’ decisions to quit, maintaining that neither Covid-19 nor politics could be definitively said to be the cause.
“The government should maybe also look into the phenomenon. It is not just universities being affected,” he said, pointing to the concurrent rise in dropouts at primary and secondary schools. “It is, after all, not an isolated topic.”