China's pollution data too hazy to know if leaders' war on smog is working
Many polluters are ignoring an edict to publish emissions details online, and numbers that are released are often incomplete, official study shows
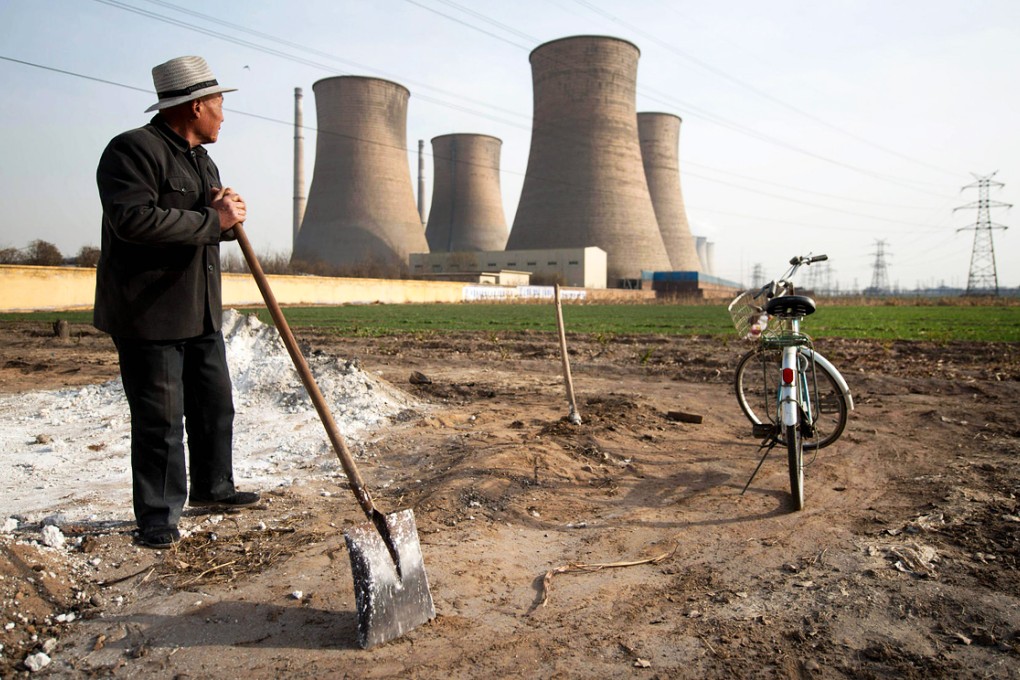

The mainland's efforts to name and shame its filthiest power stations and impose tough new emission standards are the leading weapons in President Xi Jinping's war on pollution. The world shouldn't hold its breath waiting for him to declare victory.

Yet a large LCD screen outside the facility in Xingtai , in southern Hebei province, 360km south of Beijing, showed the plant was still partly operating. It was spewing fumes at almost three times the legal limit two days after the rules were introduced, according to a reading displayed on the screen.
Flaws are evident in the data across the country, with less than half the polluters in some provinces complying with a July 2013 edict from the Ministry of Environmental Protection to publish emissions data online, according to the ministry's own study. And the numbers that are released are often incomplete or show many plants continue to emit pollutants well above the maximum levels permitted, according to an examination of the data by Bloomberg News.
"We have good standards but it's always about implementation, what happens in the real world," said Huang Wei, a climate and energy campaigner for Greenpeace in Beijing.
The mainland's environment authorities at the local level "have very little power to eliminate these little plants", she said.